Exploring transcription in oncogenesis and response to anticancer treatment
Agnese Cristini
our research area
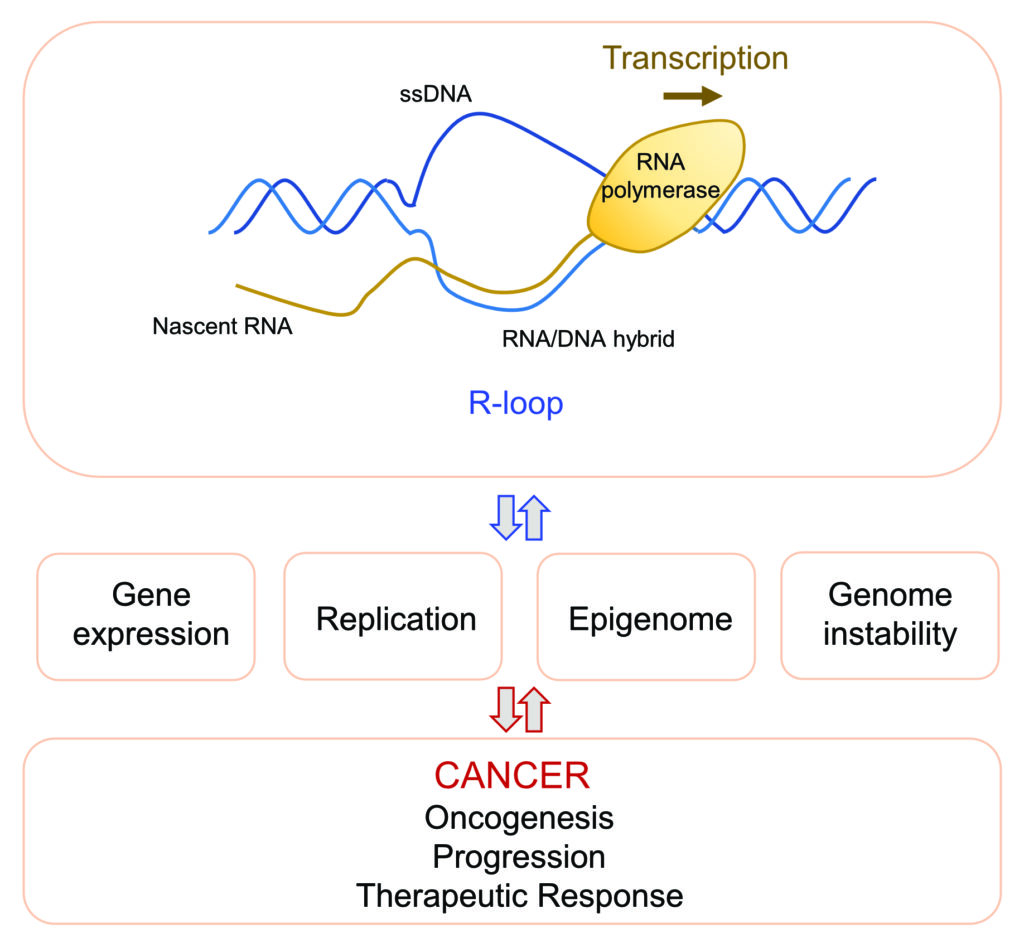
Genetic and epigenetic alterations trigger deregulated gene expression, which is a hallmark of cancer. Cancer cells are “transcriptionally addicted” to these dysregulated transcriptional programs which help sustaining tumour growth and survival. Transcription is associated with the formation of nucleic acid structures, called R-loops, which consist of an RNA/DNA hybrid and a displaced single-stranded DNA. These structures display a complex interplay with key cellular processes including gene expression, replication and maintenance of genomic and epigenomic stability, which are all involved in cancer.
Our research focuses on investigating the molecular mechanisms by which transcription contributes to cancer onset, evolution and response to anticancer therapies. For this, we employ a combination of genome-wide, high-content, biochemical, cellular and molecular approaches.
If you are interested in joining us, please contact us by email (agnese.cristini@inserm.fr) to get more information.
Keywords :
- Cancer
- Transcription
- R-loop
- Gene Expression
- Genome Instability
- DNA Damage
- Oncogenesis
- Anticancer Therapy
- Targeted Therapy
- Chromatin
- Epigenome
Group members :
- Eglantine Faget, PhD student
- Emma Lehir, PhD student
- Anaïs Pouget, Master 1 student
Alumni :
- Maïna Vienne, Research Assistant in Bioinformatics
- Elisa Spielmann, Master 2 student
- Lara Keszleri, Erasmus student
- Elisona Shyti, Erasmus student
- Ana Alvarez, Visiting PhD student
- Stella Kristensen, Erasmus student
- Jacqueline Mohr, Undergraduate DAAD student
- Fanny Wandersleb, Undergraduate DAAD student
- Jakob Freudenberger, Undergraduate DAAD student
Other team members involved
- Olivier Sordet, PhD, HDR, Research Scientist (CRCN)
- Olivier Calvayrac, PhD, Research Scientist (CRCN)
- Mathéa Géraud, Hospital-University Assistantt
- Andrea Carla Ajello, PhD student
Selected publications :
STAR Protoc. 2025 Mar 21;6(1):103662. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.103662. PMID: 40023839.
Geraud M, Fernandez Martinez L, Ajello AC, Cristini A#, Sordet O#.
Protocol for single-cell analysis of DNA double-strand break production and repair in cell-cycle phases by automated high-content microscopy. *
#Co-corresponding authors.
Nat Genet. 2023 Oct;55(10):1721-1734. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01504-w. PMID: 37735199
McCann JL*, Cristini A*, Law EK, Lee SY, Tellier M, Carpenter MA, Beghè C, Kim JJ, Sanchez A, Jarvis MC, Stefanovska B, Temiz NA, Bergstrom EN, Salamango DJ, Brown MR, Murphy S, Alexandrov LB, Miller KM, Gromak N, Harris RS.
APOBEC3B regulates R-loops and promotes transcription-associated mutagenesis in cancer.
*Co-first authors.
Nat Commun. 2022 May 26;13(1):2961. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30604-0. PMID: 35618715
Cristini A, Tellier M, Constantinescu F, Accalai C, Albulescu LO, Heiringhoff R, Bery N, Sordet O, Murphy S, and Gromak N.
RNase H2, mutated in Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome, resolves co-transcriptional R-loops to prevent DNA breaks and inflammation.
Cell Rep. 2019 Sep 17;28(12):3167-3181.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.041. PMID: 31533039
Cristini A, Ricci G, Britton S, Salimbeni S, Huang SN, Marinello J, Calsou P, Pommier Y, Favre G, Capranico G, Gromak N, Sordet O.
Dual Processing of R-Loops and Topoisomerase I Induces Transcription-Dependent DNA Double-Strand Breaks.
Cell Rep. 2018 May 8;23(6):1891-1905. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.025. PMID: 29742442
Cristini A*, Groh M*, Kristiansen MS, Gromak N.
RNA/DNA Hybrid Interactome Identifies DXH9 as a Molecular Player in Transcriptional Termination and R-Loop-Associated DNA Damage.
*Co-first authors.